Introduction
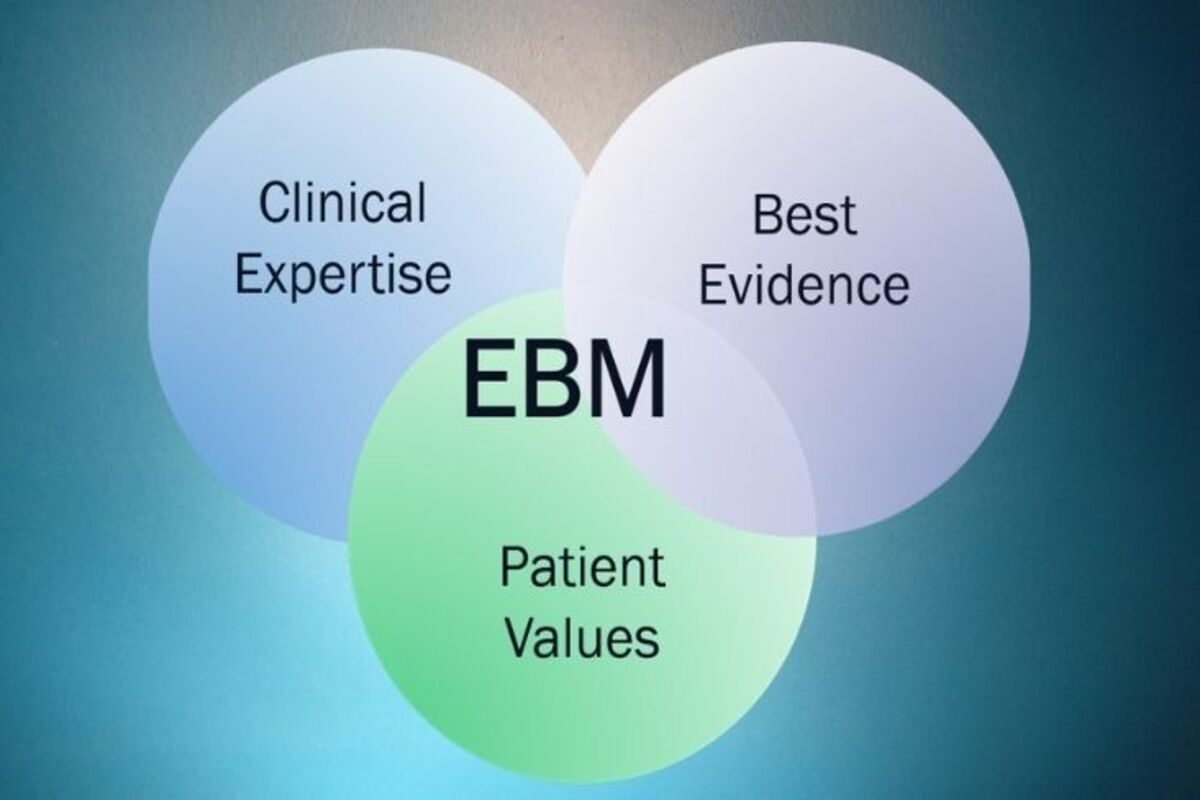
Evidence-based medicine is the system of practicing medicine in such a way that it results in improving outcomes and reduces the overall healthcare cost. Evidence-based medicine also takes care of the individual preference of the patients, along with the clinical expertise of the clinicians.
Evidence-Based Medicine
Evidence-based medicine is the multidisciplinary approach to provide the best care to the patient at the right time. Evidence-based medicine involves the use of the experience of the clinician and the updated evidence available to make the best decision related to the treatment regimen.
It is to be noted that the research article required to alter or continue the treatment strategy should be strong and fulfil the criteria to become credible evidence. This creates a basic difference between evidence-based medicine and traditional medicine.
In evidence-based medicine, the doctor and the healthcare professionals should make the best possible application of the evidence to raise the standard of patient care. The process of evidence-based medicine comprises evidence selection and knowledge translation in terms of patient care.
Evolution of the Evidence-Based Medicine
Gordon Guyatt coined the term ‘Evidence-Based Medicine’ in the year 1990. This term was first used in an article published in the year 1992 in JAMA. However, the use of evidence-based medicine started much before this.
Before evidence-based medicine, medical decisions were made based on individual clinician’s experience or the marketing strategies of pharmaceutical companies. Many clinicians disagreed with this approach and advocate for the practice, which is backed up by the latest medical knowledge.
Evidence-based medicine is based on two important pillars. While one pillar indicates the use of best healthcare practice based on concrete evidence, the other pillar ensures that the clinicians should inform in detail the new treatment to the patients so that the patient can make informed decisions.
Importance in Research and Practice
Evidence-based medicine is positively affecting all the important aspects of healthcare, which include patient care, patient’s health, and the related cost. This system of medicine has its importance in research and practice in the following manner:
Updated information to the clinicians: Evidence-based medicine requires the clinicians to read the information and latest research articles related to their therapeutic area. This helps the clinicians to remain updated with the latest evidences for treating patients.
Data for making treatment decisions: Because of the advancements in technology, and the availability of user-friendly databases, the clinicians now have access to the research data and knowledge. This helps clinicians to make informed decisions for better patient care.
Enhance the quality of overall care: Through the best-quality peer-reviewed articles, the clinicians have the data and procedures for caring for the patients. The data is reviewed by experts in the healthcare domain. This improves the overall quality of patient care.
Make the healthcare system more accountable and transparent: Patients and their relatives, many times, have concerns about the treatment strategy of the doctor. Evidence-based medicine makes clinicians more accountable and helps in improving transparency in the healthcare system.
Improves outcomes: It is one of the best effects of evidence-based medicine. A lot of data is available that indicates that if evidence-based medicine is applied logically, it will help in improving the overall healthcare outcomes.
Practicing the Evidence-Based Medicine
Information from evidence-based medicine is not readily available. The clinicians should be able to extract the information from the available evidence. For this, considerable experience and time is required. Following are the steps that help in effectively practicing evidence-based medicine:
Step I: In the first step, the clinicians should determine the problem that requires to be solved. The primary aim of problem identification should be such that solving the problem will result in improves outcomes and prevent or reduce the frequency of recurrent of the condition.
Step II: In the next step, the clinicians should search for evidence that may best solve their problems. For searching the evidence, the clinician should look for credible evidence. The sources of evidence may be categorized through an evidence-based medicine pyramid.
Step III: The clinicians then critically analyze every evidence to determine whether it aligns with the solution that needs to be determined. The clinicians should also ensure that the evidence should apply to the population under consideration.
Step IV: Once the best solution, through the evidence, is determined, the doctor may apply the solution in his clinical practice.
Step V: The clinicians should evaluate the performance of the new treatment strategy. They should measure if there is an overall improvement in health outcomes.
Conclusion
Evidence-based medicine plays an important role in research and practice. Through evidence-based medicine, clinicians can implement the best treatment regimens for their patients.